Data types: int8, int16, int32, int64
Represents a signed integer number stored with 8, 16, 32 or 64 bit.
Type syntax
int8
int16
int32
int64
Literal syntax
+/-decimal‑literal
Discussion
The number of bits determines directly the range for the respective values:
Number of bits |
Min. value |
Max. value |
|---|---|---|
8 bit |
–128 |
127 |
16 bit |
–32768 |
32767 |
32 bit |
–2147483648 |
2147483647 |
64 bit |
–2^63 |
2^63 - 1 |
The signed integer numbers must always be expressed as a sequence of digits with an optional + or - sign put in front of the number. The literals can be used within expressions wherever an int8, int16, int32 or int64 operand is expected. The type names, in turn, are designated to be used in declarations of data members. For example:
var int32 voltage = 220000; var int16 current = -100;
64-bit restrictions on WebGL (JavaScript) target
The 64-bit support depends on the features available in the particular target system. This is especially problematic when developing a GUI application for the WebGL target system. In this case the underlying JavaScript language does not support the storage of real 64-bit integer values nor it is able to perform real-64 bit arithmetic operations. In fact, JavaScript manages numbers as 64-bit floating point entities with maximally 53-bit intended to store the number (mantissa). As soon as an integer value exceeds 53-bit the precision will decline. This should be taken in account when you perform arithmetic operations with the supposed 64-bit numbers.
Even more restrictive is the case if you intend to perform bitwise operations on 64-bit operands. JavaScript reduces in such cases the operands to 32-bit causing the results of the operation to be not predictable. Therefore, when targeting WebGL you should be careful and avoid the usage of more than 53-bit in int64 operands for arithmetic operations and even 32-bit for bitwise operations.
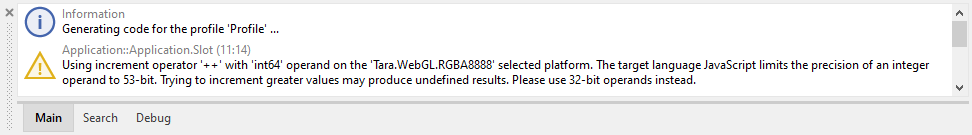
When generating code for WebGL target Embedded Wizard verifies int64 operands and reports warnings if an operation is suspect and not guaranteed to produce correct results. For example, the increment operator ++ may fail if the operand it is applied on would contain a large number. Embedded Wizard reports in such case a warning like shown below:
Instant properties
With the following instant properties you can evaluate the value of an int8, int16, int32 or int64 operand:
Instant property name |
Short description |
|---|---|
Represents the absolute value of the given operand resulting in the same (signed) data type. |
|
Represents the absolute value of the given operand resulting in the unsigned version of the operand's data type. |
Arithmetic operations
You can combine a signed integer operand with other operands to arithmetic expressions. The following table provides an overview of the possible operations:
Operator |
Short description |
|---|---|
Addition |
|
Subtraction |
|
Multiplication |
|
Division |
|
Modulo division |
Bitwise operations
You can apply bitwise operations on signed integer operands. The operations are applied on all 8, 16, 32 or 64 bits of the operand. The following table provides an overview of the possible operations:
Operator |
Short description |
|---|---|
Bitwise NOT |
|
AND |
|
OR |
|
XOR |
|
Right shift |
|
Left shift |
Comparison operations
You can compare two signed integer operands in order to test whether these are equal or not. The following table provides an overview of the possible operations:
Operator |
Short description |
|---|---|
Equality |
|
Inequality |
|
Less than |
|
Greater than |
|
Less than or equal |
|
Greater than or equal |
Type conversions
Chora reacts sensitive when mixing operands of different data types within an operation. To avoid compiler warnings or even errors you can convert the affected operands explicitly by using following conversion operations:
Conversion operations with signed integers |
|---|
Conversion between signed and unsigned integers. |
Conversion to or from a floating-point value. |
Conversion to or from an enumeration value. |
Conversion to or from a set value. |
Conversion to or from a char value. |
Formatting a string from a signed integer number. |
Parsing a string as a signed integer number. |
