Getting started with Renesas: RX65N Envision Kit (RPBRX65N)

RX65N Envision Kit (RPBRX65N).
The following article explains all necessary steps to create an Embedded Wizard UI application suitable for the RX65N Envision Kit from Renesas.
Please follow these instructions carefully and step by step in order to ensure that you will get everything up and running on your target. In case you are not familiar with Embedded Wizard, please read first the chapter basic concepts and the Quick Tour tutorial to understand the principles of Embedded Wizard and the GUI development workflow.
Prerequisites
First, make sure you have all of the following items:
Hardware components
★RX65N Envision Kit from Renesas (RPBRX65N) (Part Number RTK5RX65N2C00000BR)
★USB cable to connect the board with your PC
Software components
★Embedded Wizard Studio Free or Embedded Wizard Studio Pro
If you want to use the Free edition of Embedded Wizard Studio please register on our website and download the software.
As a customer, please visit the Embedded Wizard Download Center (login/password required) and download Embedded Wizard Studio Pro.
★Embedded Wizard Build Environment for RX65N Envision Kit
To evaluate Embedded Wizard on the mentioned target, you can download the suitable Build Environment from the following link:
![]() RX65N-EnvisionKit-BuildEnvironment-V12.00.00.01.zip
RX65N-EnvisionKit-BuildEnvironment-V12.00.00.01.zip
As a customer, please visit the Embedded Wizard Download Center (login/password required) and download the latest version of the Build Environment and your licensed Platform Package libraries or source codes.
★Optional: Renesas e2 Studio for Windows
Installing Tools and Software
★Step 1: Install the latest version of Embedded Wizard Studio.
★Step 2: Install the GCC for Renesas GNURX Toolchain.
★Step 3: Install the Renesas Flash Programmer.
★Step 4: Unpack the provided Embedded Wizard Build Environment for RX65N Envision Kit to your local file system (e.g. C:\RenesasRX\RX65N-EnvisionKit). Please make sure to use a short working folder path because e2 Studio (to be more precise: Eclipse) has restrictions regarding the file path length.
★Step 5: Take a text editor and open the file StartGccBuildEnvironment.bat that you will find in the root directory of the Build Environment. At the beginning of the file, the following environment variable has to be set to the installation path of the GCC for Renesas GNURX Toolchain:
•GCC_For_Renesas_Path - Absolute path of your installed GCC for Renesas GNURX Toolchain (Step 2).
★Step 6: Take a text editor and open the file FlashDownload.cfg that you will find in the subdirectory \Application\FlashDownload of the Build Environment. At the beginning of the file, the following environment variable has to be set to the installation path of the Renesas Flash Programmer:
•RenesasFlashProgrammerPath - Absolute path of your installed Renesas Flash Programmer (Step 3).
Exploring the Build Environment
The provided Embedded Wizard Build Environment for RX65N Envision Kit contains everything you need to create, compile, link and flash an Embedded Wizard UI application for the Renesas RX65N target. After unpacking, you will find the following subdirectories and files:
•StartGccBuildEnvironment.bat - This script file is provided to start a windows command line to build your GUI applications for the target. Don't forget to set the path of your installed compiler.
•\Application - This folder contains ready-to-use projects to compile and link an Embedded Wizard generated UI application. They are used for all provided examples and they can be used to build your own UI applications.
•\FlashDownload - This folder contains a script to load the created binaries into the flash of your target by using the Renesas Flash Programmer tool. Don't forget to set the path of your installed Renesas Flash Programmer within the file FlashDownload.cfg.
•\GeneratedCode - This folder is used to receive the generated code from an Embedded Wizard UI project. All template projects are building the UI application out of this folder. You can create your own UI project and generate the code into the subdirectory \GeneratedCode without the need to adapt the project.
•\Project - This folder contains the prepared projects for GCC (make) and Renesas e2 Studio.
•\Source - This folder contains the files main.c and ewmain.c. There you will find the initialization of the system and the main loop to drive an Embedded Wizard GUI application. The file ewconfig.h contains general configuration settings for the target system, like memory ranges and display parameter and configuration settings for the Embedded Wizard Graphics Engine and Runtime Environment.
•\Examples\<ScreenSize> - This folder contains a set of demo applications prepared for a dedicated screen size (480x272 pixel). Each example is stored in a separate folder containing the entire Embedded Wizard UI project. Every project contains the necessary profile settings for the Renesas RX65N target. The following samples are provided:
•\HelloWorld - A very simple project that is useful as starting point and to verify that the entire toolchain, your installation and your board is properly working.
•\ColorFormats - This project demonstrates that every UI application can be generated for different color formats: RGB565, LumA44 and Index8.
•\ScreenOrientation - This demo shows, that the orientation of the UI application is independent from the physical orientation of the display.
•\DeviceIntegration - This example shows the integration of devices into a UI application and addresses typical questions: How to start a certain action on the target? How to get data from a device?
•\GraphicsAccelerator - This application demonstrates the graphics performance of the target by using sets of basic drawing operations that are executed permanently and continuously.
•\BezierClock - The sample application BezierClock implements a fancy digital clock and timer application with animated digits. The application uses vector graphics to render dynamically the different digits for clock and timer. The change from one digit to another is handled by moving the vector points to get a smooth transition animation.
•\BrickGame - The sample application BrickGame implements a classic "paddle and ball" game. In the game, a couple of brick rows are arranged in the upper part of the screen. A ball travels across the screen, bouncing off the top and side walls of the screen. When a brick is hit, the ball bounces away and the brick is destroyed. The player has a movable paddle to bounce the ball upward, keeping it in play.
•\ClimateCabinet - The ClimateCabinet demo shows the implementation of a control panel for a climatic exposure test cabinet. The user can define a heating time, a nominal temperature and humidity, a dwell time and the final cooling time.
•\PaperCutter - This demo shows the implementation of a paper cutting machine, where the user can define the pagination and format of the paper as well as the cutting speed and the amount of papers. The application contains many rect effects and fade-in/fade-out effects to change dynamically the layout of the screen.
•\WashingMachine - This demo shows the implementation of a washing machine with a couple of fancy scrollable list widgets to choose the washing program and parameters. The speciality of this sample application is the magnification effect of the centered list items and the soft fade-in/fade-out effects.
•\WaveformGenerator - This WaveformGenerator demo application combines waveforms with different amplitudes and frequencies. The implementation shows the usage of vector graphics to draw a curve based on a list of coordinates.
•\PlatformPackage - This folder contains the necessary source codes and/or libraries of the Renesas RX Platform Package: Several Graphics Engines for the different color formats (RGB565, LumA44 and Index8) and the Runtime Environment (in the subdirectory \RTE).
•\TargetSpecific - This folder contains all configuration files and platform specific source codes. The different ew_bsp_xxx files implement the bridge between the Embedded Wizard UI application and the underlying board support package (Renesas RX hardware drivers) in order to access the graphics accelerator, the display or the touch interface.
•\ThirdParty - This folder contains third-party source codes and tools:
•\Make - This folder contains a make tool to build the entire GUI application via command line.
•\Renesas - This folder contains the necessary Renesas RX65N software used for the Embedded Wizard UI applications (initialization, drivers).
Creating the UI Examples
For the first bring up of your system, we recommend to use the example 'HelloWorld':
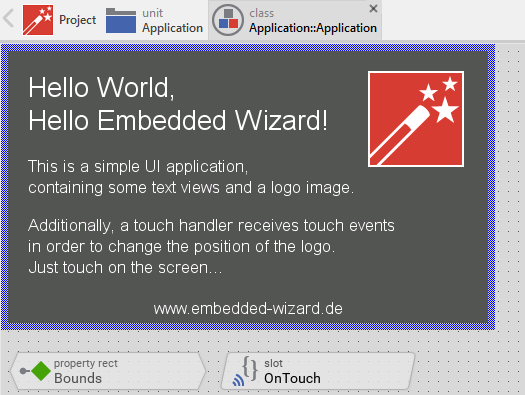
Example 'HelloWorld' within Embedded Wizard Studio.
The following steps are necessary to generate the source code of this sample application:
★Navigate to the directory \Examples\<ScreenSize>\HelloWorld.
★Open the project file HelloWorld.ewp with your previously installed Embedded Wizard Studio. The entire project is well documented inline. You can run the UI application within the Prototyper by pressing Ctrl+F5.
★To start the code generator, select the menu items - or simply press F8. Embedded Wizard Studio generates now the sources files of the example project into the directory \Application\GeneratedCode.
Compiling, Linking and Flashing
The following steps are necessary to build and flash the Embedded Wizard UI sample application using the GCC for Renesas GNURX toolchain:
★Navigate to the top level of the Build Environment.
★Open StartGccBuildEnvironment.bat - as a result, a windows command line window should open. In case there are error messages, please edit the file and double-check the path setting.
★Set the DIP switches on your RX65N Envision Kit to SW1-1 ON, SW1-2 OFF, SW4-1 OFF, SW4-2 OFF and connect the board via USB with your PC.
★Now start compiling, linking and flashing:
make make install
If everything works as expected, the application should be built and flashed to the Renesas RX65N target.

Example 'HelloWorld' running on RX65N Envision Kit.
All other examples can be created in the same way: Just open the desired example with Embedded Wizard Studio, generate code and rebuild the whole application using simply:
make install
Please always take care that you bring the DIP switches to the correct position before and after flashing.
Creating your own UI Applications
In order to create your own UI project suitable for the Renesas RX65N target, you can create a new project and select the RX65N Envision Kit project template:
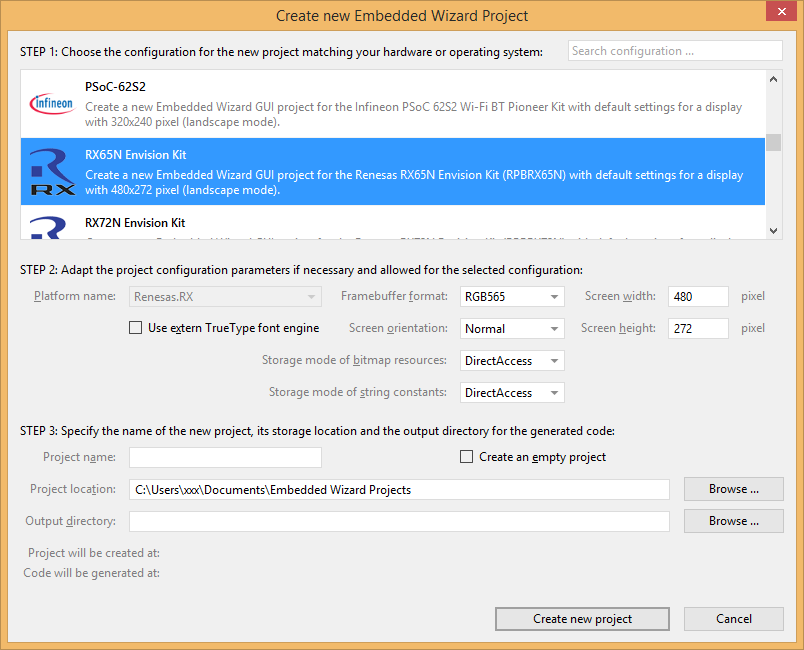
As a result you get a new Embedded Wizard project, that contains the necessary Profile attributes suitable for the RX65N Envision Kit board:
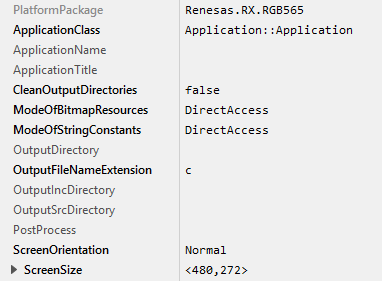
The following profile settings are important for your target:
★The attribute PlatformPackage should refer to the Renesas RX Platform Package.
★The attribute ScreenSize should correspond to the display size of the RX65N Envision Kit.
★The attributes ModeOfBitmapResources and ModeOfStringConstants should be set to DirectAccess. This ensures that resources are taken directly from flash memory.
★The attribute OutputDirectory should refer to the \Application\GeneratedCode directory within your Build Environment. By using this template, it will be very easy to build the UI project for your target.
★The attribute CleanOutputDirectories should be set to true to ensure that unused source code within the output directory \Application\GeneratedCode will be deleted.
★The attribute PostProcess should refer to \Application\Project\e2Studio\RX65N-EnvisionKit\e2_Studio_ew_post_process.cmd if you are working with Renesas e2 Studio. In case of the GCC for Renesas GNURX toolchain leave it blank.
Now you can use the template project in the same manner as it was used for the provided examples to compile, link and flash the binary.
After generating code, please follow these steps, in order to build your own UI application:
★Start the batch file StartGccBuildEnvironment.bat. Again, a windows command line window should open.
★Set the DIP switches on your RX65N Envision Kit to SW1-1 ON, SW1-2 OFF, SW4-1 OFF, SW4-2 OFF. Connect the board via USB with your PC.
★Start compiling, linking and flashing:
make install
★Finally, disconnect the board, set the DIP switches to SW1-1 OFF, SW1-2 OFF, SW4-1 OFF, SW4-2 OFF and connect the board again via USB with your PC.
Most of the project settings are taken directly out of the generated code, like the color format or the screen orientation. All other settings can be made directly within the file ewconfig.h, which contains general configuration settings for the target system.
Using Renesas e2 Studio
If you want to use the Renesas e2 Studio toolchain instead of the GCC for Renesas GNURX toolchain, please follow these instructions:
The subdirectory \Application\Project\e2Studio contains a template project that is commonly used for all provided Embedded Wizard examples. All Embedded Wizard examples will store the generated code within the common \Application\GeneratedCode folder.
IMPORTANT
Please ensure that you have selected Support for RX Devices in the section Device Families and GCC for Renesas RX in the section Additional Software / GCC Toolchains & Utilities during the installation of Renesas e2 Studio.
The following steps are needed to establish this automatic project import:
★Open the desired Embedded Wizard example project.
★Select the Profile and set the attribute PostProcess to the file ..\..\Application\Project\e2Studio\RX65N-EnvisionKit\e2_Studio_ew_post_process.cmd.
After the Embedded Wizard code generation the installed post process will adapt the .cproject XML file. All necessary libraries and include paths (depending on the color format and screen rotation) will be set automatically.
The given e2 Studio example under \Application\e2Studio contains a workspace which has all adaptions for an Embedded Wizard project. For using this within Renesas e2 Studio do following steps:
★Open Renesas e2 Studio and select the directory \Application\Project\e2Studio as workspace directory.
★To import the C project, select the menu item File - Import and choose General - Existing Projects into Workspace and press Next.
★Choose Select root directory - Browse and select the directory \Application\Project\e2Studio\RX65N-EnvisionKit.
★Press Finish.
★To compile the project select Project - Build Project.
★Set the DIP switches on your RX65N Envision Kit to SW1-1 ON, SW1-2 OFF, SW4-1 OFF, SW4-2 OFF and connect the board via USB with your PC.
★Choose the build-in debug function (green bug button) for debugging the application on your target.
If the color format or the screen orientation was changed, please do a clean in Renesas e2 Studio.
When using Renesas e2 Studio the console output is redirected automatically to the build-in tool Renesas Debug Virtual Console - This terminal connection can be used for all trace statements from your Embedded Wizard UI applications or for all debug messages from your C code.
Console output
In order to receive error messages or to display simple debug or trace messages from your Embedded Wizard UI application, the serial output is forwarded to the e2 Studio Virtual Debug Console. Per default this build-in console is shown within the e2 Studio.
In case that it is necessary to open this console manually, please do following step:
★Add the Renesas Virtual Debug Console by pressing .
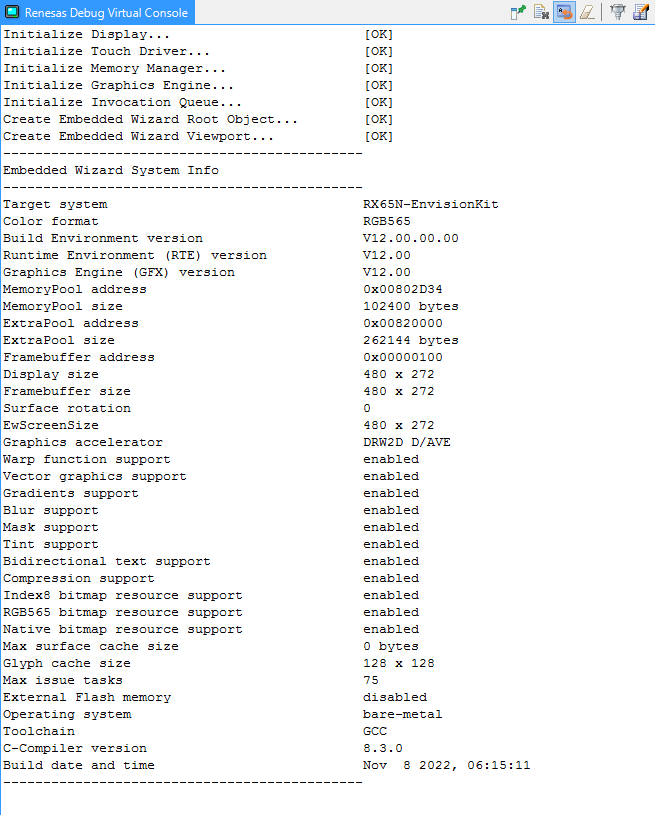
The Virtual Debug Console can be used for all trace statements from your Embedded Wizard UI applications or for all debug messages from your C code.
Custom specific hardware
In order to bring-up an Embedded Wizard generated UI application on your Renesas RX65N custom hardware, you can use the provided Embedded Wizard Build Environment for RX65N Envision Kit as a template.. The file ewconfig.h contains target specific settings that have to be adjusted to your particular hardware. Furthermore, the subdirectory \TargetSpecific contains all the platform specific source codes. Assuming that your custom hardware is similar to the RX65N Envision Kit, the following adaptations or configurations are typically necessary:
★System clock (ew_bsp_system.c) - The first and the important step is to configure the system and peripheral clock. Depending on your hardware you can use the internal or external clock as source. The Embedded Wizard UI application runs independent from the chosen system frequency, however, with a slow system clock, all components need more time for their tasks (e.g. display refresh).
★USART (ew_bsp_console.c) - Typically, the USART configuration just requires a new pinout according your hardware layout. The usage of the serial connection is highly recommended in order to get status and debug messages during runtime.
★GLCDC (ew_bsp_display.c) - The GLCDC is an integrate display controller which allows you to connect many different display types to a RX65N device. Here you have to adjust the interface to your display. It is important to adjust your pinout, polarity, timings, color format and layer settings according your dedicated display.
★Touch (ew_bsp_touch.c) - If your application requires touch support, you can integrate a given touch driver provided by the touch controller manufacturer or write your own. As a result the current touch position should be returned.
As soon as these steps are done, you can create your own GUI application or use one of the provided examples. If the size of your display is different compared to the display of the RX65N Envision Kit (480x272 pixel), please adapt the attribute ScreenSize of the UI project and the size of the framebuffer within the file ewconfig.h accordingly.
In case you want to change the operating system, please adapt the all functions within the file ew_bsp_os.c to your particular operating system. Furthermore, adapt the makefile/projectfile accordingly.
Release notes
The following section contains the version history of the Build Environment (including Graphics Engine and Runtime Environment) for RX65N Envision Kit. These release notes describe only the platform specific aspects - for all general improvements and enhancements please see the Embedded Wizard release notes.
Version 12.00.00.00
★Enhanced system configuration: The set of macros used to configure the target system has been enhanced within the file ewconfig.h. All macros are now described in the article target configuration.
★Operating system wrapper (ew_bsp_os.c): All operating system services used within the Build Environment are now grouped together and implemented within the file ew_bsp_os.c. This simplifies the adaptation to other (realtime) operating systems. The functions EwBspClockTickIncrement() and EwBspClockGetTicks() are replaced by EwBspOsSystickHandler() and EwBspOsGetTicks(). Please verify that the system tick is working properly in case you are updating from previous versions.
★Multi-Thread, Multi-Task check functionality: All relevant top-level Runtime Environment and Graphics Engine functions perform now a test whether the function is called in context of the original GUI thread/task. For this purpose the test compares the current CPU stack address with the address area known as used for GUI thread/task stack. The stack memory area is provided to the Embedded Wizard application within the file main.c by using the function EwSetStackAddressArea(). The size of the stack area is defined by the macro EW_GUI_THREAD_STACK_SIZE in the file ewconfig.h. The test functionality can be disabled by the macro EW_DONT_CHECK_THREAD_CONTEXT in the file ewconfig.h.
★Communication between threads and tasks: The Runtime Environment has been enhanced by new functions EwInvoke() and EwInvokeCopy(). These functions register user's own implemented C functions to be called in context of GUI thread/task. These functions are explicitly allowed to be called from any foreign thread or even from interrupt service routines. The new macro EW_INVOCATION_QUEUE_SIZE in the file ewconfig.h determines the size of the invocation queue in bytes. The initialization of the invocation queue is done in EwInit() by calling the function EwInitInvocations(). The deinitialization of the invocation queue by using EwDoneInvocations() can be found in EwDone(). The main loop EwProcess() that drives the entire Embedded Wizard GUI application is enhanced by the new function EwProcessInvocations().
★System initialization: The configuration of Runtime Environment and Graphics Engine is now done in EwInit() by using the new functions EwConfigRuntimeEnvironment() and EwConfigGraphicsEngine().
★System information: The function EwPrintSystemInfo() is now determining the current configuration of Runtime Environment and Graphics Engine by using the new functions EwGetRuntimeEnvironmentInfo() and EwGetGraphicsEngineInfo(). The version numbers are printed according to the new version numbering scheme. The layout of the entire message printed to the console is rearranged.
★Immediate garbage collection: The test function EwTestImmediateReclaimMemory() performs a simple test for the correct function of the immediate garbage collection. If the application is compiled with the macro EW_USE_IMMEDIATE_GARBAGE_COLLECTION and the the stack area is specified by using EwSetStackAddressArea(), the function EwTestImmediateReclaimMemory() verifies the correct operation. This is added to EwInit() in the file ewmain.c.
★Cache invalidation: The function GfxCreateSurface() in the file ewextgfx.c is adapted to invalidate the data cache for the complete address range of the pixel data to avoid that cache is written after modifications by graphics hardware.
★Touch initialization: The initialization of the touch driver is improved to avoid potential division by zero errors during runtime in case that touch initialization has failed.
★Color channel order: The default color channel order in compressed bitmap resources has changed from ABGR to ARGB. This avoids an additional color channel reordering during the loading (decompression) of the bitmap resources.
★Device integration example: The example DeviceIntegration and the DeviceDriver.c/h files have to be adapted to show the usage of the new features: A separate worker-thread is created to provide simulated ADC data to the GUI. The functions EwInvoke() and EwInvokeCopy() are used from the work-thread and the hardbutton interrupt service routine (ISR). The example supports OS and bare-metal. The previously used functions DeviceDriver_Init(), DeviceDriver_Done() and DeviceDriver_ProcessData() are presented as deprecated approach or bare-metal.
★Changed to Graphics Engine (GFX) and Runtime Environment (RTE) V12.00.
★Changed to GCC for Renesas RX 8.3.0.202202.
★Changed to Renesas e2 Studio 2022-10 (22.10.0).
★Changed to Renesas e2 Studio 2022-10 (22.10.0) - Support for RX Devices.
★Changed to Renesas Flash Programmer v3.10.00.
Version 12.00.00.01
★Optimization of single-buffered display update to achieve higher framerates.
